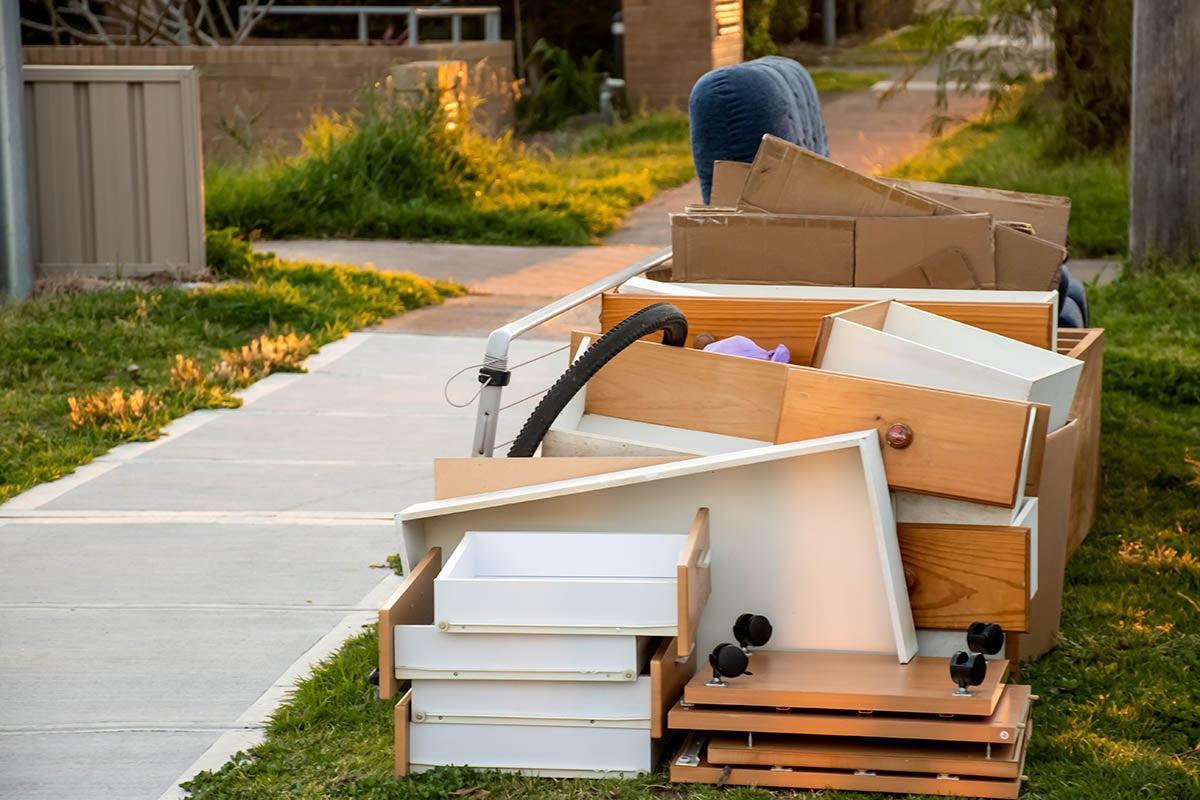
The term "fast furniture production" refers to the mass production of furniture that is made quickly and at a low cost. However, this process has a significant negative impact on the environment. It consumes large amounts of natural resources such as wood, water, and energy, leading to deforestation, water depletion, and greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the transportation of materials and furniture across the globe contributes to air pollution, which is harmful to human health.
Deforestation is a major consequence of fast furniture production. The high demand for wood in this process leads to trees being cut down faster than they can regrow, resulting in deforestation and habitat loss for many species. Unsustainable sourcing of wood also contributes to this problem.
Fast furniture production has a significant carbon footprint. The production and transportation of furniture generate greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to climate change. The transportation of raw materials and finished products across the globe further worsens this issue.
Another issue with fast furniture production is waste. The production of cheaply made and non-durable furniture often leads to products becoming obsolete or unusable quickly. This results in furniture being discarded and ending up in landfills. The disposal of furniture in landfills is problematic as it takes hundreds of years to break down, releases toxic chemicals, and contributes to pollution and habitat loss.